Aneurysms | Austin Texas Aneurysm Experts
Artery Aneurysm Treatments
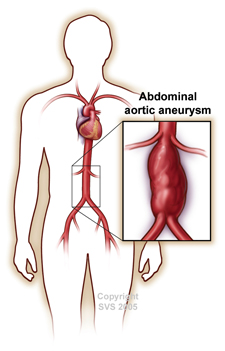
An aneurysm is an abnormal bulge in the wall of an artery. Aneurysms can occur in any artery of the body, with the most common locations being within the abdomen, pelvis, chest, and legs. The most common artery affected by aneurysms is the aorta, which is also the largest artery in the body. Aneurysm are usually not symptomatic until they rupture. They are usually diagnosed by physicians either by physical examination or through radiology / x-ray studies, such as CT scans, MRI, or artery ultrasounds. The CT scan to examine an aneurysm is referred to as a CTA (CT angiogram). Similarly a MRI to examine an aneurysm is referred to as a MRA (MR angiogram). These studies are performed in everyone that is to undergo a repair in order to get detailed imaging of the anatomy in order to plan the repair.
Aneurysms usually develop wherever blood vessel pressure is strongest and where the vessel wall is weakest , i.e., in areas where blood vessels divide and branch off to other parts of the body. Aneurysms are extremely risky and dangerous. If an aneurysm bursts, it can cause life-threatening internal bleeding. Some aneurysms also are prone to blood clots developing within them. Approximately 15,000 Americans die each year from ruptured aortic aneurysms alone. Ruptured aortic aneurysms are cited as the 10th leading cause of death among men over 50 in the US. Artery blood clots can form in an aneurysm without warning and block blood flow to vital parts of your body. These complications can lead to heart attack, damage or death of an organ, stroke, loss of limb (arm or leg) and even sudden death.
Aneurysms can be caused by illness or injury. But many people with aneurysm are genetically predisposed to aneurysms due to the poor elasticity of their arteries. Many people with aneurysm have other known family members who have also been diagnosed with aneurysm disease. Other risk factors for development of aneurysm include: aging, plaque buildup, cigarette smoking, high blood pressure, history of heart disease or peripheral artery disease, and blood infections. Cigarette smoking is one of the most significant risk factors for the development of many types of arterial aneurysms. The chemicals within the cigarettes circulate within the blood, damaging the lining and wall of the blood vessels. This leads to weakness and thinning of the blood vessel wall that leads to the aneurysm development.
Aneurysm Treatment & Aneurysm Repair Procedures
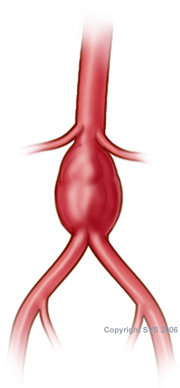
Once an aneurysm is identified, treatments will vary depending on the size and location of the aneuryms. Some aneurysms may be initially treated with medical management, including blood pressure control and close surveillance with periodic examination and radiology studies. This is typically the case for smaller aneurysm.
Other aneurysms may require repair by a physician. Aneurysms are most commonly repaired by vascular surgeons, who are considered aneurysm experts. Treatment could include artery catheterization in which stents or embolization coils (“plugging” of the artery) are placed to prevent the aneurysm from receiving blood flow. Other aneurysms may require traditional “open” surgical operation due to their anatomic location. The outlook on surgical intervention or catheterization is generally excellent if the aneurysm is caught in time. Which type of repair is performed may also partially be determined by the age of the patient.
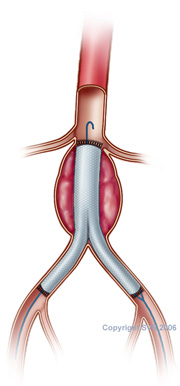
There are two common approaches to aortic aneurysm repair (the most common aneurysm type). 1) traditional “open” or surgical repair and “stent-graft” or 2) endovascular repair using catheters. During open aneurysm repair, the weakened part of your artery will often be replaced with a hose-like rubbery material which will allow the blood to pass easily through it. Essentially, the damaged blood vessel is replaced by a strong artificial blood vessel.
Other types of open traditional surgery may involve ligation of the abnormal blood vessel and bypass around the diseased area. Certain types of aneurysms, such as aneurysm of the spleen, may be treated by actually removing the organ along with the aneurysm. Since the spleen is not vital to normal body function in an adult, the spleen can often be sacrificed while removing the aneurysm. More advanced and less invasive methods of spleen aneurysm repair include the use of embolization coils or stent-grafts.
During endovascular repair, an endovascular stent-graft repair is placed with catheters. Under x-ray guidance, a small narrow catheter is threaded through the arteries by punctures or incisions in the groin area or arms. This stent procedure is considered a less invasive. This endovascular method tends to be associated with less risk and faster recovery. Surgery time depends on several factors including area of aneurysm, aneurysm size, and aneurysm type.
Eligibility For Repair of Aneurysms
Most individuals with aneurysms are candidates for repair with either an open or endovascular surgery approach. The best method to repair an aneurysm and the type of surgical approach to take depends on several factors, including the risk of rupture, the location and shape of the aneurysm, the age of the patient, and the general health of the patient. An stent is more likely to require periodic maintenance and closer follow-up than a traditional open surgical procedure. Your vascular specialist will help you decide what the best method of treatment is for your particular situation.
Post-Surgery / Recovery after Aneurysm Repair
Traditional open surgical repair of aneurysms typically involves a longer hospitalization and longer recovery time when compared to stent-grafts. You would expect to be in the hospital for around 5 days after “open” surgery for an aneurysm repair. Because of the less invasive nature of the endovascular stent-graft repair or catheterization procedures, patients’ hospital stay is often reduced to 1-2 days. Recovery time varies by the health and age of the patient and their level of strength.
Hardening of arteries / atherosclerosis is associated with aneurysms. So many patient with aneurysms also have underlying plaque disease in their heart and other blood vessels. They also tend to have a higher risk of heart attacks and strokes. Lowering blood pressure and cholesterol / lipid levels may reduce the risk of developing aneurysm. Additionally, eating foods lower in fat, cholesterol, and calories, aerobic exercise, quitting smoking, and maintaining a healthy body weight are all changes that could also lower the risk of developing another aneurysms.
Risks of Aneurysm Repair
As with any surgical procedure there are risks associated with aneurysm repair surgery. However, greater risk lies in ignoring problems that could be symptomatic of an aneurysm or deeper health issue. Patients should actively discuss symptoms and concerns with their healthcare provider. If surgery or treatment has been decided on, personal health or lifestyle issues (i.e. smoking, diet, and exercise) that could be factors in the success of their surgeries must be discussed with their healthcare providers.
For more information about aneurysms or aneurysm repair or to arrange an ultrasound screen for aneurysm disease, please contact our Vascular Center at (512) 339-9100. We have offices in both Austin & Round Rock Texas.






